
Fax: (860) 430-9693
Glastonbury, CT 06033
The labrum is a cartilage ring that forms part of the hip or shoulder socket and helps stabilize the joint. Like any type of musculoskeletal tear, labral tears occur on a spectrum, from minor to severe, and lead to pain and a loss of function in the joint. Thankfully, most labral tears can be treated non-invasively using the methods we provide here at Valley Sports Physicians & Orthopedic Medicine. If you’ve been diagnosed with a labral tear, or you just think you might have one, give us a call today so we can start providing the targeted care you need for treating labral tears in Glastonbury, CT.

Symptoms of labral tears can include:
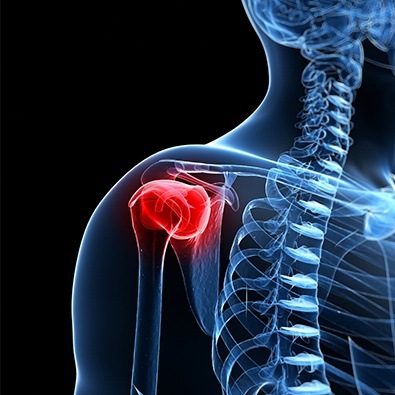
The Diagnosis of a labral tear usually requires an MRI. But the history and physical exam can provide important clues as to whether the labrum is the culprit. You cannot see labral tears on x-rays. And often the tear is too deep inside the joint to be seen on diagnostic ultrasound. At Valley Sports Physicians & Orthopedic Medicine, if we suspect that the labrum is the cause of the pain, we may perform a diagnostic injection by putting a small amount of anesthetic into the joint under ultrasound guidance (an almost painless procedure). If you get a significant temporary reduction of your pain, then the labrum may be the cause. However, if the injection doesn’t help, then it’s much less likely that the labrum is causing your pain.
Treatment for labral tears partly depends on the nature and severity of the tear. For early or mild tears physical therapy usually helps. If therapy fails, then Regenerative Medicine treatments such as PRP and stem cells may be tried. Larger and more complex tears often require surgical repair. However, the vast majority of labral tears in people over 40 years old do NOT require surgery—the pain most often either is coming from a different problem or a combination of the labral tear and another problem.