
Fax: (860) 430-9693
Glastonbury, CT 06033
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (or CTS) is an entrapment of the median nerve at the base of the wrist. The arm is supplied by 3 major nerves: the radial nerve, the median nerve, and the ulnar nerve (all of which arise from the neck). The median nerve travels down the front of the forearm. When it reaches the wrist, it passes through a tunnel called the Carpal Tunnel. The tendons that flex or curl the fingers (the flexor tendons) also pass through the Carpal Tunnel deep to the nerve. The roof of the tunnel is formed by a thick ligament band called the flexor retinaculum. We offer solutions for treating carpal tunnel syndrome in Glastonbury, CT at Valley Sports Physicians & Orthopedic Medicine.


The classic symptoms of CTS include numbness and/or tingling in the palmar aspect of the thumb, index and middle fingers. Occasionally the thumb side of the ring finger is involved. If these fingers are not involved, then it's very highly unlikely that it's Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. The pinky is NEVER affected in CTS (it's supplied by the ulnar nerve). And the back of the hand also is almost never involved in CTS. Though rare, some people may experience CTS-related symptoms all the way up the arm to the shoulder. The most common presentation is the hand falling asleep during the night while sleeping. Patients typically report that they hang their hand off the side of the bed and shake it to wake it up.
Learn More About Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms

The most common cause of CTS is repetitive strain injury, usually from work-related activities that involve a lot of repetitive wrist movements or computer work, such as dental hygienists, accountants, assembly line workers, seamstresses/tailors, etc. However, other common causes include pregnancy and thyroid disease (particularly underactive or hypothyroidism). In addition, a history of injury to the wrist such as a fracture or dislocation that decreases the size of the carpal tunnel may make one more susceptible to developing CTS.

The history alone should give a strong clue to the possibility of CTS. A physical exam is important, but often the exam is normal, especially in early or milder cases. Electrodiagnostic testing, namely EMG/NCV studies (electromyography and nerve conduction velocity) are considered the "gold standard" for diagnosing CTS. But this is an invasive uncomfortable test, and the results can be highly dependent on the skill of the physician performing the test. Also, the test can be normal in the early phases of the condition. In more recent years, diagnostic ultrasound has emerged as a highly sensitive non-invasive way of actually looking at the nerve and measuring it. A swollen enlarged nerve indicates CTS. Ultrasound has the advantage of being able to be performed right in the office in a matter of minutes. X-rays cannot diagnose CTS but they can be helpful to identify other problems such as arthritis. MRI is almost never needed.
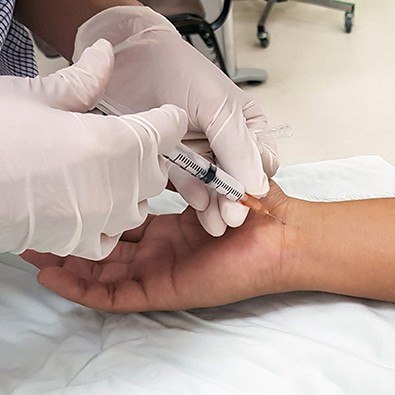
Treatments for CTS partly depend on the severity of the condition. Mild CTS can be treated with stretching, wrist splints, and physical therapy. Occasionally a cortisone injection can help reduce the swelling and irritation of the nerve. Activity modification and adjusting the work environment to reduce the stress on the wrist is also important to prevent a recurrence. Moderate and more severe cases of CTS usually need a more aggressive treatment approach. In our office, we utilize a special painless injection technique known as hydrodissection to free up the pinched nerve and reduce swelling and inflammation. It's highly effective and has almost no associated risks and side effects. In more stubborn cases the area around the pinched median nerve is injected with PRP (platelet-rich plasma) or other biologic agents to promote healing. Very severe cases of CTS that have resulted in muscle loss usually need surgery.

If you suspect that you have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, then you likely have a lot of questions. What should I do next? How long will treatment take? How much will it cost? Below, we’ve answered some of the most popular questions we hear from our patients regarding CTS. After reading this over, if there is anything else you’d like to know, we invite you to give our team a call.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a very specific condition, and in order to diagnose it, your doctor at Valley Sports Physicians will perform a number of tactile tests on your wrist and hand to determine whether or not your symptoms are due to the median nerve becoming compressed. We may also utilize diagnostic ultrasound so we can get a better look at the tissues around the nerve. Just because you have chronic hand and wrist pain doesn’t automatically mean you have CTS!
In most cases, no, and the condition will likely worsen over time if you try to just “tough it out.” If you continue to engage in the repetitive motion that led to the condition in the first place, symptoms and pain will only become worse. Even if your CTS is due to an acute injury, not getting professional treatment may prevent your body from fully healing. The best move is to come see us as soon as you think you have CTS—acting quickly will help us address the condition early using the most conservative methods.
The time necessary to fully address someone’s CTS will vary from patient to patient based on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment used. Rest, ice, and wearing a brace can usually help minor CTS go away over a matter of weeks, but for more advanced cases, treatment may take months and involve multiple rounds of prolotherapy, PRP, or stem cell injections. When you come to see us, we’ll evaluate your condition and discuss your treatment options so you’ll have a fleshed-out idea of what your specific recovery process will be like.
The cost of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome treatment will vary from patient to patient based on the procedures used and the frequency they are utilized. More traditional methods like wearing a brace and physical therapy will cost less versus cutting-edge regenerative medicine techniques like stem cell therapy, for example, though they likely will require more time. We understand that your budget and schedule matter, so our team will work with you to formulate a treatment plan that helps you get results as efficiently as possible without forcing you to throw your budget out the window.